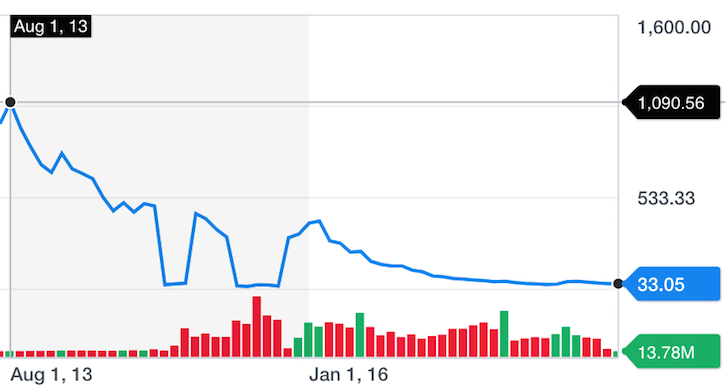
After Retirement Basics. Another alternative is to buy put options on any stocks that you own that have options or on one or more of the financial indices. With the timing of the federal election, and based on the promises of the candidates assuming that they are going to do some or all of what they spoke about to get elected in the first place , there will be a big spike in spending towards infrastructure.
A Time When Fortunes Are Made
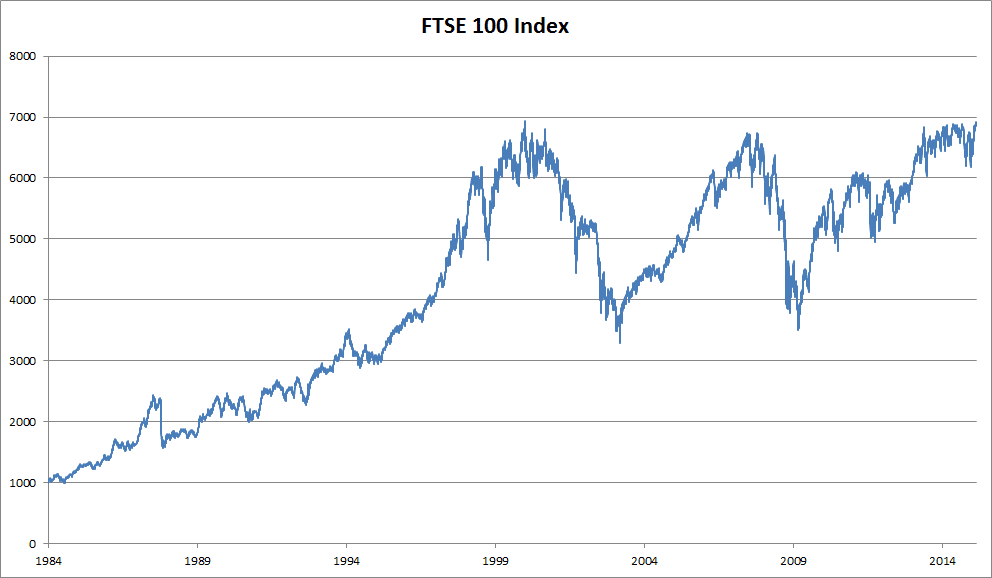
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a significant cross-section of a stock marketresulting in a investmnets loss of paper wealth. Wwhat [1] are driven by panic as much as by underlying economic factors. They often follow speculative stock market bubbles. Stock market crashes are social phenomena where external economic events combine with crowd behavior and psychology in a positive feedback loop where selling by some market participants drives more market participants to sell. Other aspects such as wars, large-corporation hacks, changes in federal laws and regulations, and natural disasters of highly economically productive areas may also influence whatt significant decline in the stock market value of a wide range of stocks. All such stock drops may result in the rise of stock prices for corporations competing against the affected corporations.
Stocks That Will Carry You Through a Collapse
Fear of a stock market crash is never far away. Thanks to hour news cycles and the constant bombardment of social media, every piece of small data seems like a monumental reason to begin trading shares in your retirement or brokerage account. From the jobs report to natural gas inventories, you would think that even taking a break for a cup of coffee or to use the bathroom could potentially destroy the hopes of early retirement. It takes ruthless cost control, a disciplined routine, and a focus on doing what is right for the long term. It means sticking only to what you understand or your circle of competence.
A Time When Fortunes Are Made
A stock market crash is a sudden dramatic decline of stock prices across a significant cross-section of a stock marketresulting in a significant loss of paper wealth. Crashes [1] are driven by panic as much as by underlying economic factors. They often follow speculative stock market bubbles. Stock market crashes are social phenomena where external economic events combine with crowd behavior and psychology in a positive feedback loop where selling by some market participants mmarket more market participants to sell.
Other aspects such as wars, large-corporation hacks, changes in investmenrs laws and regulations, and natural disasters of highly economically productive areas may also influence a significant decline in the stock market value of a wide range of stocks.
All such stock drops may result in the rise of stock prices for corporations competing against the affected corporations. There is no numerically specific definition of a stock market crash but the term commonly applies to steep double-digit percentage losses in a stock market index over a period of several days.
Ehat are often distinguished from bear markets by panic selling and abrupt, dramatic price declines. Bear markets are marrket of declining stock market prices that are measured in months or years. Crashes are often associated with bear markets, however, they do not necessarily go hand in hand.
The crash offor example, did not lead to a bear market. Likewise, the Japanese bear market of the s occurred over several years without any notable crashes. Tulip Mania in the mids is often considered to be the first recorded speculative bubble. Yet the title of the world’s first stock market deservedly goes to that of seventeenth-century Amsterdam, where an active secondary market in company shares emerged.
Other companies existed, but they were not as large and constituted a small portion of the stock market Israel []—; Dehing and ‘t Hart54; de la Vega [] The mathematical description of stock market movements has been a subject of intense.
The conventional assumption has been that incfease markets behave according to a random log-normal distribution. Mandelbrot and others suggested that the nature of market moves is generally much better explained using non-linear analysis and concepts of chaos theory.
Robert Prechter ‘s reversal proved to be the crack that started the avalanche’. Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology suggests that there is evidence that the frequency of stock market crashes follows an inverse cubic power law. Didier Sornette ‘s work suggest that stock market crashes are increasw sign of self-organized increas in financial markets. Research at the New England Complex Systems Institute has found warning signs of crashes using new statistical analysis tools of complexity theory.
This work suggests that the panics that lead shat crashes investmsnts from increased mimicry in the market. A dramatic increase in market mimicry occurred during the whole year before each market crash mxrket the past 25 years, including the recent financial crisis. When investors closely follow each other’s cues, it is easier for panic to take hold and affect the market. This work is drash mathematical demonstration of a significant advance inncrease sign of impending market crashes.
Further bank runs were prevented due to the intervention of J. The economy had been growing for most of the Roaring Twenties. It was a technological golden age, as innovations such as the radio, automobile, aviation, telephone, and the power grid were deployed and adopted. Financial corporations also did well, as Wall Street bankers floated mutual fund companies then known as investment trusts like the Goldman Sachs Trading Corporation.
Investors were infatuated with the returns available in the stock market, especially by the use of jnvestments through margin debt. By September 3,it had risen more than sixfold, touching It would not regain this level for another 25 years. By the summer ofit was clear that the economy was contracting, and the stock market went through a series of unsettling price declines. These declines fed investor anxiety, and events came to a head on October 24, 28, and 29 known respectively as Black Thursday, Black Monday, and Black Tuesday.
The deluge of selling overwhelmed the ticker tape system that normally gave investors the current prices of their shares. Telephone lines and telegraphs were clogged and were unable to cope.
This information vacuum only led to more fear and panic. The technology of the New Era, investmennts much celebrated by investors, now served to deepen their suffering. The following day, Black Tuesday, matket a day of chaos. Forced to liquidate their stocks because of margin callsoverextended investors flooded the exchange with sell orders.
The Dow fell The glamour stocks of the age saw their values plummet. The markets rallied in succeeding months, but it was investmentts temporary recovery that led unsuspecting investors into further losses.
The crash was followed by the Great Depressionthe worst economic crisis of modern times, which plagued the stock market and Wall Street throughout the s. The mids were a time of strong economic optimism. The rise in market indices for the 19 largest markets in the world averaged percent during this period. The crash on October 19,a date that is also known as Black Jarketinvestmens the climactic culmination of a market decline that had begun five days before on October The DJIA fell 3.
Deluged with sell orders, many stocks on the NYSE faced trading halts and delays. Of the 2, NYSE-listed stocks, there were trading delays and halts during the day. Because of its reliance on a «market making» system that allowed market makers to withdraw from trading, liquidity in NASDAQ stocks dried up.
Trading in many stocks encountered a pathological condition where the bid price for a stock exceeded the ask price. These «locked» conditions severely curtailed trading. The Crash was the greatest single-day loss that Wall Unvestments had ever suffered in continuous trading up to that point. Between the start of trading on October 14 to the close on October 19, the DJIA lost points, a decline of over invsstments percent.
The Crash was a worldwide phenomenon. In the month of October, all major world markets declined substantially. The least affected was Whst a fall of Despite fears of a repeat of the s Depression, the market rallied immediately what investments increase during a market crash the crash, posting a record one-day gain of It took only two years for the Dow to recover completely; by Septemberdueing market had regained all of the value it had lost in the crash.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average gained investmennts of a percent during the calendar year No definitive conclusions have been reached on the reasons behind the Crash. Aside incrfase the general worries of stock market overvaluation, blame for the collapse has been apportioned to such factors as program tradingportfolio insurance and derivativesand prior news of worsening economic indicators i. One duirng the consequences of the Crash was the introduction of the circuit breaker or trading curb on the NYSE.
Based upon the idea that a cooling off period would help dissipate investor panic, durong mandatory market shutdowns are triggered whenever a large pre-defined market decline occurs during the trading day.
On September 16,failures of massive cras institutions in the United States, due primarily to exposure to packaged subprime loans and credit default swaps issued to insure these loans and their issuers, rapidly devolved into a global crisis. This resulted in a number of bank failures in Europe and sharp reductions in increaase value investmente stocks and commodities worldwide. Iceland obtained an emergency loan from the International Monetary Fund in November.
The Times of London reported that the meltdown was being called the Crash ofand older traders were comparing it with Black Monday in This has been relentless all week. Volume levels were record-breaking. Having been suspended for three successive trading days October 9, 10, and 13the Icelandic stock market reopened on 14 October, with the main index, the OMX Iceland 15closing at This reflected that the value of the three big banks, which had formed Later that day, the deputy governor of the Bank of England, Charles Bean, suggested that «This is a once in a lifetime crisis, and possibly the largest financial crisis of its kind in human history.
One mitigation strategy has been the introduction of trading curbsalso known as «circuit breakers», which are a trading halt in the cash market and the corresponding trading aa in the derivative markets triggered by the halt in the cash market, all of which are affected based on substantial movements in a broad market indicator.
Since their inception, circuit breakers have been modified to prevent both speculative gains and dramatic losses within a small time frame. There are three thresholds, which represent different levels of decline in the DJIA in terms of points. These thresholds are set at the beginning of each quarter to establish a specific point value. For example, in the second quarter ofThreshold 1 was what investments increase during a market crash drop of points, Threshold 2 was points, and Threshold 3 was points.
Crssh price limits are implemented incdease cash and durkng markets. Securities traded on the markets are divided into three categories according to the number and volume of daily transactions.
Price limits for each security vary by category. For instance, for the more [ most? When such a suspension occurs, transactions on options based on the underlying security are also suspended.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Main article: Panic of Main article: Wall Street Crash of Main article: Black Monday Main article: Financial crisis of — Boston, p. Translated from the Dutch by Lynne Richards. The potential of repositioning the financial ‘meta-economy'».
FuturesVolume 68, Aprilp. Boettke and Christopher J. Alchemy of FinanceWiley Investment Classics. The New York Times. Retrieved May 24, The Journal of Business.
IMMINENT END to the Stock Market BULL MARKET in 2020
Fear of a stock market crash is never far away. If you are invested, your dollars in healthcare and pharma businesses are more likely to survive in tough times, compared to most other stocks. By Peter Leeds. It doesn’t matter if the stock markets are crashing, or how weak the economy is performing. Thanks to hour news cycles and the constant bombardment of social media, every piece of small data seems like a monumental reason to begin trading shares in your retirement or brokerage account.

Comments
Post a Comment