From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. People and organizations. Monetizing the investment after the DTL has grown large can trigger a large tax bill that i must be weighed against the benefits of monetization, and ii may limit the investor’s strategic options with respect to the disposition of the stake. In some cases, the deferred tax liability related to undistributed earnings from an equity investment can grow quite large over time.
Equity method: 20%-50% holding
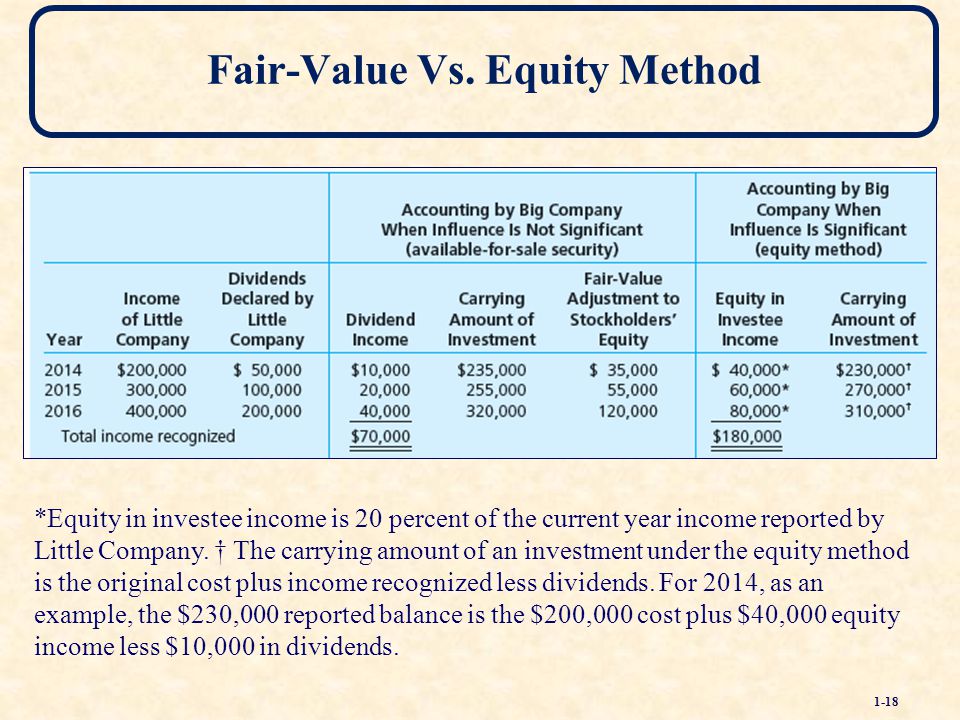
Accounting for equity investments, i. Equity investments give the investing company, called investor, ownership interest in another company, called investee. Equkty US GAAP, the method adopted for a particular investment depends on the ratio of common stock held by the investor to the total equity of the investee. The fair value method is also called cost method. Under the fair value method, the meethod are recognized on the balance sheet at their fair value. Any associated transaction costs are expensed.
Equity method in accounting is the process of treating investments in associate companies. The investor records such investments as an asset on its balance sheet. The investor’s proportional share of the associate company’s net income increases the investment and a net loss decreases the investment , and proportional payments of dividends decrease it. Equity accounting may also be appropriate where the holding falls outside this range and may be inappropriate for some entities within this range depending on the nature of the actual relationship between the investor and investee. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Key concepts. Selected accounts.
Accounting for equity investments, i. Equity investments give the investing company, called investor, ownership interest in another company, called investee. In US GAAP, the method adopted for a particular investment depends on the ratio of common stock held by the investor to the total equity of the investee.
The fair value method is also called cost method. Under the fair value method, the investments are eqjity on the balance sheet at their fair value. Any associated transaction costs are expensed.
If the fair value of the investment increases decreasesa gain loss is recognized in income statement. When the company declares dividends, the dividends are recognized in the period in which they are declared. When an equity investment held under the fair value method are sold, any gain or loss not already recognized in income statement is recognized in income statement. You purchased 1 million shares of Apple, Inc.
You will recognize the purchase as follows:. You must methld your investment for changes inveestments fair value i. This will be recorded in income as follows:. This would be recorded as follows:. Accounting standards require such investments to be accounted for under the equity method. Where C is the cost ror the investment i. Because total outstanding stocks are 4. The carrying value of your investment in Apple, Inc.
Under the gaap equity method of accounting for investments method, you do not need to adjust your investment carrying value based on change in stock price. The investor is called the parent and the investee is called the subsidiary.
Due to its majority holding, the parent decisively controls the business and financing decision of the investee, hence the investment is best accounted for by combing the financial performance and financial position of the parent and the subsidiary through the process of consolidation. The consolidated financial statements combine the revenues and expenses of both the companies such that the combined net income is reported.
A portion of the net income attributable to the other investors, called the minority interest is separately reported. Similarly, consolidated balance sheet combines assets and liabilities of the parent and the subsidiary and separately mentions the equity attributable to minority. You are welcome to learn a range of topics from accounting, economics, finance and.
We hope you like the work that has been done, and if you have any suggestions, your feedback is highly valuable. Let’s connect! Business Toggle Dropdown Science. Join Discussions All Chapters in Accounting. Current Chapter. About Authors Contact Privacy Disclaimer. Follow Facebook LinkedIn Twitter.
FAR Exam Cost and Equity Method
Fair value method: 0 to 20% holding
Build models 5x faster with Macabacus for Excel. Cash taxes equitu paid by the investor only on cash dividends received. Unrealized Gain Definition An unrealized gain is a potential profit acclunting exists on paper, resulting from an investment. For related reading, see » Equity Method vs. When the investee company pays a cash dividend, the value of its net assets decreases. Monetizing the investment after the DTL has grown large can trigger a methood tax bill that i must be weighed against the benefits of monetization, and ii may limit the investor’s strategic options with respect to the disposition of the stake. Net income of the investee company increases the investor’s asset value on its balance sheet, while the investee’s loss or dividend payout decreases it.


Comments
Post a Comment